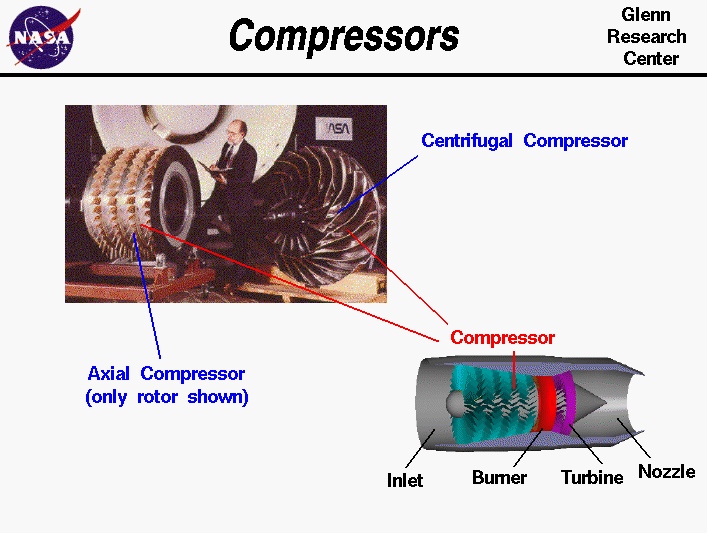
Most modern passenger and military aircraft are powered by gas turbine engines, also known as jet engines. Although there are many different types of gas turbine engines, all turbine engines have certain parts in common. The compressor turbine engines, increase the pressure of the incoming air before it enters the combustor. Compressor performance has a significant influence on total engine performance.
According to the figure above, there are two primary compressor types: axial and centrifugal. The compressor on the left side of the picture is referred to as an axial compressor because the flow through it runs parallel to the axis of rotation. The compressor on the right is called a centrifugal compressor because the flow through it is turned perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Small turbojets and turboshaft engines still employ centrifugal compressors, which were originally utilized in the first jet engines. Axial compressors are commonly used in modern large turbojet and turbofan engines.
What led you to switch to axial compressors? Pressure can be raised by a factor of 4 with an average single-stage centrifugal compressor. A similar average, single-stage axial compressor increases the pressure by only 1.2 factors. Linking together several stages and producing a multistage axial compressor is relatively simple. In the multistage compressor, the pressure is multiplied from row to row (8 stages at 1.2 per stage, giving a factor of 4.3).
The production of an efficient multistage centrifugal compressor is much more challenging due to the need to duct the flow back to the axis at each stage. The flow being turned perpendicular to the axis causes a centrifugal compressor engine to be wider and have a greater cross-sectional area than an axial engine. This creates additional undesirable drag on the aircraft. For these reasons, most high-performance, high-compression turbine engines use multistage axial compressors. If you only need a small amount of compression, a centrifugal compressor will be easier to use.
Reference: https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/compress