Solar energy still accounts for a little less than 3% of the electricity generated in the United States largely due to the high cost of producing solar cells
The most common type of energy storage in the electricity network is pumped hydropower.
Storage allows solar energy to contribute to the power supply even when the sun does not shine. It can also help reduce variability in how solar energy flows through the grid.
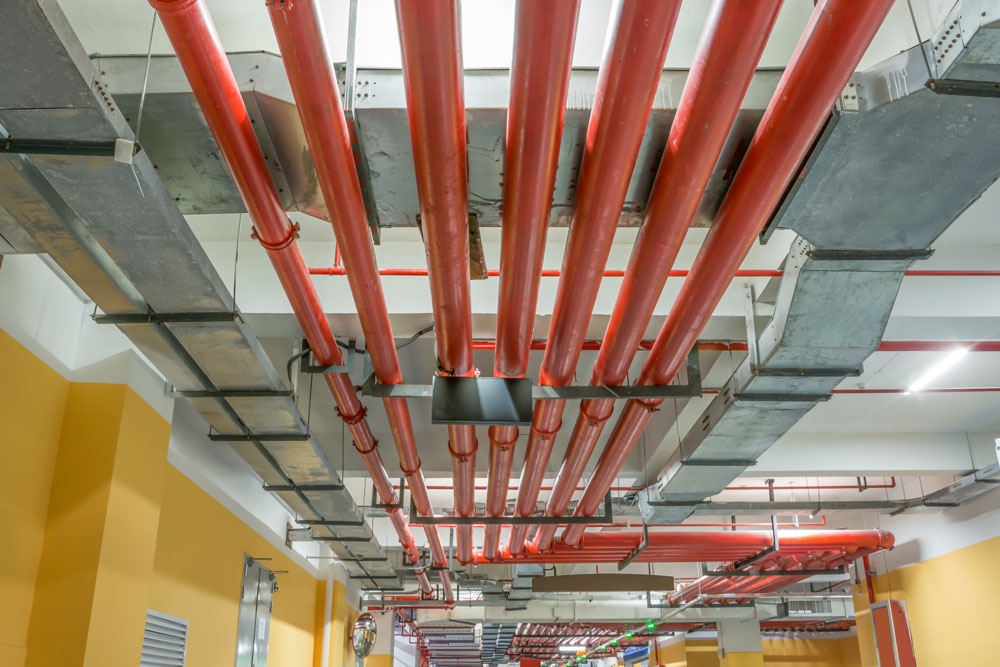
Emergency and Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) layouts, as well as fire suppression systems, can provide valuable details on a building’s possible behavior and the scope of an incident.
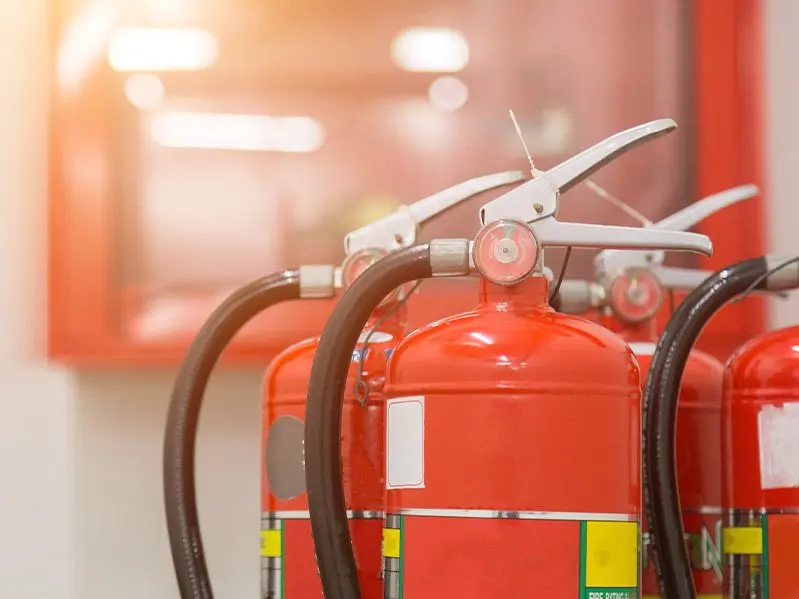
Fire outbreaks and gas leaks in processing plants can cause significant damage and loss of life.
Inert gas suppression systems use argon and nitrogen gases and their mixtures as an extinguishing agent and are based in the principle of reducing the oxygen concentration inside the protected hazard.
Twin-Agent Fire Protection means the “twin-attack” capabilities of dry chemicals and foam firefighting agents.
With a carbon dioxide system, the clean-up costs and downtime associated with a CO2 discharge are negligible. It has been used as an effective fire extinguisher since the early 1900s.
Monocrystalline solar panels are the most efficient type of panel; polycrystalline and thin-film solar panels are other common solar panel types that offer lower efficiency.
Solar panel efficiency is a measurement of a solar panel’s ability to convert sunlight into usable electricity.