An electric machine combines all the components of a diesel generator to convert energy from one source into another form of energy. The operation of a power generator involves taking mechanical energy and converting it into electrical energy.
The Diesel Generator gives the alternator mechanical energy, which is then converted into an electrical current by a magnetic field and electromagnetic induction. To get the most out of this product, it’s crucial to understand the Diesel Generator Parts.
Electric Generator
An electric generator is a machine that produces electrical power, which can be utilized for a variety of uses, from small power appliances to large industrial machines. A popular option is to use grid power generated from fossil fuels or wind turbines, combined with a steam turbine in a power plant.
There are many generator types, including petrol generators, portable generators, inverter generators, home generators that may work on natural gas, standby generators to hold power on during an outage, and very large industrial generators. The main focus of this article is to explain diesel generators, also known as gunshots, their working principles, and their fundamental components.
Diesel Generators
Different users such as homes, schools, hospitals, and industrial centers receive continuous or standby power from diesel generators. They have the option to be either small enough to be carried easily or large enough to fit in houses. Nonetheless, there is a unit that is suitable for every user. Fuel energy is converted into electrical energy diesel generators to provide power to loads.
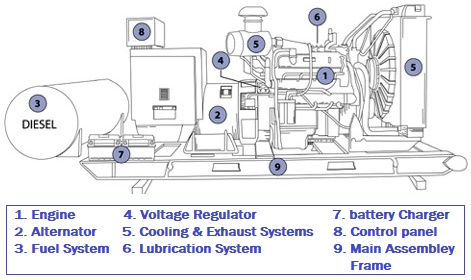
Diesel Generator Parts
At least nine components make up each diesel generator. Here, we will explain the different parts of a diesel generator. The main components of the diesel generator are identified and numbered in the figure below.
10 Parts of the Diesel Generator are:
- Diesel Engine
- Alternator
- Fuel System
- Voltage Regulator
- Cooling System and Exhaust System
- Lubrication System
- Battery Charger
- Control Panel
- Main Assembly Frame
- What Is B Check In DG?
Diesel Engine
Mechanical energy can be obtained from a diesel engine. The engine’s size has a direct impact on the amount of electrical energy produced. The engine size will increase if the desired output power is higher. The diesel engine type is also commonly used in cars, trucks, or large vehicles.
Alternator
The alternator is the component responsible for producing power. Electromagnetic induction is involved in this situation, as outlined in the following.
The rotor is one of the most significant components in an alternator, which has many complex parts. It consists of a shaft that rotates due to the mechanical energy provided by the engine, with multiple permanent magnets installed around it, and consequently, a magnetic field is created.
The stator is another important component of the alternator that is continuously spun around this magnetic field. A set of electrical conductors that are tightly wound over an iron core. The principle of electromagnetic induction states that if an electrical conductor remains stationary and a magnetic field surrounds it, an electrical current is generated.
To summarize, the alternator uses mechanical energy generated by the diesel engine to drive the rotor and create a magnetic field around the stator, which causes an alternating current.
Fuel System
The fuel system is generally composed of a fuel tank and a pipe that connects it to the engine. As previously mentioned, diesel can be directly supplied to the engine to initiate the process. The fuel tank size eventually determines how long a generator can be active.
Most silent canopy generators come with fuel tanks on the base of the electric generator as a standard feature. If a larger fuel capacity is required, we can design and produce a bespoke extended base fuel system or attach it to an extra freestanding bulk fuel tank. A silent diesel generator has a steel or plastic surround to decrease noise.
For larger power generator plans that require the generator to be placed in an acoustic room, separate fuel systems are usually located either inside or beneath the room, or sometimes both.
The voltage regulator is the most complex component of an electric generator. This part has an explanatory purpose, which is regulating the voltage output. The voltage regulator is a highly detailed process that is not covered in the current article.
It ensures that the generator generates electricity at a steady voltage. The engine speed determines the extreme fluctuations that occur in the absence of a voltage regulator. The unsteady power supply cannot be controlled by any of our electrical devices. Thus, the goal of using this part is to ensure smooth and uniform operation.
Cooling System and Exhaust System
These two parts, both have essential functions. The responsibility of the cooling system is to prevent the generator overheating. The coolant is released in the generator, which counteracts all the engine and alternator extra heat energy. The coolant then takes all of this heat through a heat exchanger and discharges it outside the generator.
The exhaust system operates similarly to the car exhaust. It captures any gases produced by the diesel engine, enters them through the piping system, and removes them from the Genset.
Lubrication System
The lubrication system is a part that connects to the engine and pumps oil into it to ensure every part works smoothly and does not grind against other parts. Without a suitable lubrication system, the machine will break down.
Battery Charger
A diesel engine requires a tiny electrical motor to help put it into action. The small motor works with a battery, which needs to be charged.
Control Panel
This part is just in the case of controlling and operating the generator. This has every controlling object, including the start button, a frequency switch, an engine fuel indicator, a temperature indicator of the coolant, and much more, enabling the user to do different works or check certain things.
The control panel starts and terminates the generator, and monitors the engine and alternator to implement monitoring, maintenance, and control. The control panel ensures everything runs properly. It can also provide synchronizing for parallel work activation.
Main Assembly Frame
Every generator needs to be held in some way, and this is the main frame of the assembly. It houses the whole generator and is where all the different diesel generator parts are made onto.
It holds everything together, and it might be an open design – or closed (canopied) for extra safekeeping and sound attenuation. The outdoor generators are usually housed in a protective frame that is weatherproof for damage prevention.
What Is B Check In DG?
B-check is done once a week or after (300-350) hours of running. The following parameters should be examined in this sort of check: * Replace the oil. * Replace the oil, fuel, and bypass filters. * Replace the air filter. * Replace the water separator if necessary. In diesel engines, the most typical coolant is water.
Conclusion
You became familiar with how a diesel generator works and all the diesel generator parts. In short, the diesel engine supplies the mechanical energy of the alternator, which is then converted to an electrical current in the presence of a magnetic field and electromagnetic induction.
Reference: Diesel Generator Parts